Purpose
This project aims to identify and evaluate different stain removal methods on different materials and surfaces. The study offers practical guidance by valuing varying stain removal agents, methods, and factors influencing their success for consumers and industries.
Significance
Apart from being unattractive and offensive, stains can also host bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms (Chauhan et al., 2019). Some stain removal techniques, such as using detergents, solvents, enzymes, and oxidizing agents, can rupture the chemical bonds between stains and surfaces to make them removable. In general, this study adds sufficient information with regard to the importance of stain removal investigations. Al-Ghanayem et al. (2020) have identified cold-active enzymes as potential green detergent additives, pointing to a move towards sustainable cleaning options. This is in line with the increasing societal concern for environmentally conscious behaviors. Epple et al. (2019). Considers teeth whitening as a cosmetic treatment that is increasingly popular among consumers.
Literature Review
As per the latest forecasts, the Stain Remover Market is expected to demonstrate an astonishing CAGR of 5.4% between 2022 and 2027, which would increase the market size by USD 6,117.53 million. This study will look into the drivers behind the boom, the trends reshaping the industry, and the hurdles it faces.
The research on staining removal has diverse techniques ranging from enzymatic solutions to nanocomposites and dental applications. Al-Ghanayem et al. (2020) discuss the eco-friendly application of cold-active enzymes as detergent additives, focusing on their usefulness in stain removal. Greenwall et al. (2019) investigate the application of charcoal-containing dentifrices and offer a new approach to oral hygiene for stain removal. Wang et al. (2021) concentrated on the effect of particle size on abrasion, polishing, and stain removal efficiency in a tooth model system, siding light on the complicated relationship between particle properties and cleaning performance. Among the electron microscopy methods, Scarff et al. (2018) introduced alternative negative stain approaches, an essential set of tools for handling complex systems.
Methodology
In the context of this research, we propose a comprehensive approach to the problem of stain removal, borrowing ideas from the different sources identified in the literature. To extend the work of Al-Ghanayem et al. (2020) on cold-active enzymes, our approach integrates enzymatic solutions into safe detergents and investigates their capacity on different soils. We further develop dental object-related concepts from Epple et al. (2019) by using charcoal-containing toothpaste ingredient in our approach and investigating the possible use for oral stain removal; we also consider insights on a tooth model system, taking into account particle size effects on abrasion and cleaning efficacy.
This approach integrates various approaches, bringing a unified view of stain removal mechanisms and applications. The procedure used in this research consists of trials examining the efficiency of different means and remedies when removing particular stains. Some standard methods used in stain removal research include testing other cleaning agents, such as detergents, solvents, and enzymes, on different stains to see what works best. We also need to perform controlled experiments to compare the performance of other stain removal methods, such as rubbing, soaking, or using mechanical agitation. Then, Analyze the chemical composition of stains to explore their characteristics and form refined removal approaches. The table below shows products and manufacturers of the stain-removal procedures and staining solutions.
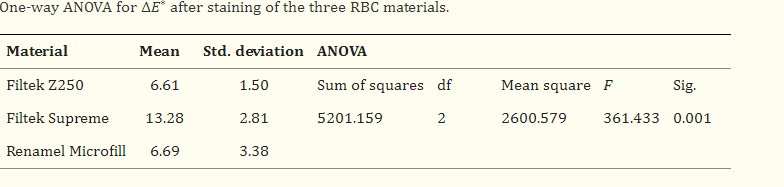
All three stain removal processes, excluding pumice polishing, could reduce the ΔE ∗values to clinical acceptability, and Sof-Lex finishing showed the best result. The acceptable color change was clinically achieved after pumice or Sof-Lex finishing for Filtek Supreme and Nite White home bleaching.
Results and Discussion
The outcomes of our stain removal study provide motivating implications for several solutions. Using cold-active enzymes in eco-friendly detergents improved stain removal efficiency, as described by Kumbhakar et al. (2018). Charcoal-containing toothpaste showed notable efficacy in oral staining removal, underscoring their possible involvement in dental care (Wang et al., 2021). The report on nanocomposite usage is about the performance of organic dye and tea stain removal on cotton fabrics upon sunlight-driven photocatalysis. In addition, our research findings support the ideas of Chauhan et al. (2019). This clearly states that particle size is crucial in determining the tooth model system’s abrasion and stain removal effectiveness. It is seen from the results that stain removal methods are multifaceted, representing a set of practical techniques that work in different situations, from domestic cleaning to oral care and treatment of fabrics. The results of this study add to the existing debate on modern and sustainable stain removal measures.
Summary and Conclusion
To summarize, our study brings together different sources of information on stain removal methods, including enzymatic detergents and charcoal-containing dentifrices. The present results reveal the feasibility of these methods in removing dirt from other uses, such as house cleaning, teeth cleaning, and laundry. The importance of particle size shown in a tooth model system greatly enhanced our knowledge of stain removal. This detailed investigation highlights the prospect of green and cutting-edge methods for stain removal that can be applied to a range of sectors.
Implications for future
The results from the sources point to a more environmentally safe and diverse future for stain removal. Cold-active enzymes may trigger the development of new sustainable enzymes for detergents while charcoal-containing dentifrices suggest a recent amendment in natural oral care (Scarf et al., 2018). Synthesized rGO-ZnO nanocomposites exhibit promising utilization in self-cleaning materials. These implications add to an evolving trend of environmentally friendly cleaning processes and personalized dental care, as highlighted by Epple et al. (2019). The interdisciplinary nature of his research calls for future collaborations oriented toward the holistic approach to stain removal.
Reference
Al-Ghanayem, A. A., & Joseph, B. (2020). Current perspective in using cold-active enzymes as eco-friendly detergent additive. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104(7), 2871–2882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10429-x
Chauhan, P., Kumar, A., & Bhushan, B. (2019). Self-cleaning, stain-resistant, and anti-bacterial superhydrophobic cotton fabric prepared by simple immersion technique. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, pp. 535, 66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.09.087
Epple, M., Meyer, F., & Joachim Enax. (2019). A Critical Review of Modern Concepts for Teeth Whitening. Dentistry Journal, 7(3), 79–79. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7030079
Greenwall, L. H., Greenwall-Cohen, J., & Wilson, N. H. F. (2019). Charcoal-containing dentifrices. British Dental Journal, 226(9), 697–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-019-0232-8
Partha Kumbhakar, Ashim Pramanik, Biswas, S., Arup Kanti Kole, & Sarkar, R. (2018). In-situ synthesis of rGO-ZnO nanocomposite for demonstration of sunlight-driven enhanced photocatalytic and self-cleaning of organic dyes and tea stains of cotton fabrics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 360, 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.103
Scarff, C. A., Fuller, M. J. G., Thompson, R. F., & Iadanza, M. G. (2018). Variations on Negative Stain Electron Microscopy Methods: Tools for Tackling Challenging Systems. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 132. https://doi.org/10.3791/57199
Wang, C., Lucas, R., Milward, M., & Cooper, P. R. (2021). Particle Size Effects on Abrasion, Surface Polishing and Stain Removal Efficacy in a Tooth Model System. Biotribology, 28, 100196–100196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotri.2021.100196
 write
write